Product Description:
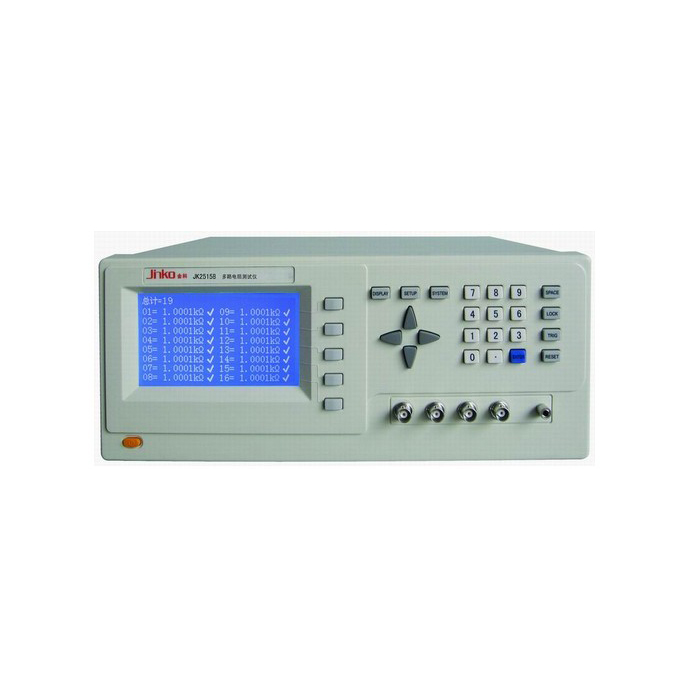
JK2515B-8S multiplex resistance scanning tester (8) using 240*128 lattice LCD disy, can be used for transformer, motor, switch, relay and other types of multiplex resistance synchronous test, Instrument
测量范围0.0001Ω~19.999kΩ,Instrument产生高精度恒流经被测件进行四端点测量,有效地扣除了引线误差,适合用户作高精度测量;由于使用 Dc test and
Up to ten groups of fast scanning test, especially suitable for copper resistance measurement of various transformers and inductors; The user can perform two kinds of sorting, that is, the upper/lower limit sorting of the resistance directly disyed value and Δ% sorting. In addition,
Single point or scan two zero clearing calibration modes; Test changes in speed (fast, slow); Full state, full set value of power protection and other functions are also greatly convenient for users to test the product
Performance Characteristics :
User-friendly operation interface, easy operation and maintenance
A single machine can scan up to 32 channels. Each channel has a sorting setting
Standard RS-232C interface
Product parameters:
Highest resolution: |
10μΩ |
Single channel speed: |
6 times per second,12 times per second |
Range mode |
Manual, automatic, range hold |
Zero clearing function: |
Short circuit |
Test end: |
5 terminal |
Disy mode: |
Direct reading |
Sorting function: |
Top pass, bottom pass, pass |
Interface: |
With RS232 interface |
Sort: |
Direct reading分选(Dire) |
Alarm mode: |
1:. Turn off the alarm (Clo)
|
Note: Above or below is unqualified |
|
Dimension (width * depth * height) : |
35*37*14cm |
Multichannel scanning sub-signal selection mode:
A: All sweep results, take 16 channels as an example: all 16 channels can only be in the same upper limit and the same lower limit, set the upper and lower limit value range (only in the same range) beyond the range to determine whether qualified or unqualified output signal (high level, low level)
B: Scan the results successively. Take the 16-channel as an example: set the upper and lower limit value range for each channel (only in the same range), and can classify the output signal (high level, low level) qualified or unqualified, and then enter the next channel to test the results.
C: The results are obtained after all scanning. Take 16 channels as an example: set different upper and lower limit value ranges for each channel (only in the same range). The results are obtained after all 16 channels are scanned to determine whether the signal is qualified or unqualified (high level, low level)